Comparative SEM Analysis Study of Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) Nanoparticles Synthesized by Sol-Gel Method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.61343/jcm.v3i02.130Keywords:
Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂) nanoparticles, Sol-Gel Method, SEM Analysis, Anatase Phase, Particle sizeAbstract
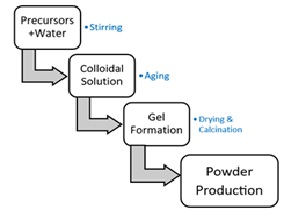
This paper describes the comparative SEM Analyses study of various samples of nanoparticle Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) synthesized by the Sol-Gel method with different changes in the parameters. Titanium dioxide is not very reactive with chemicals and doesn't harm the environment, so it is widely used as a colour in industry. It comes in three forms: anatase, rutile, and Brookite. Scanning electron microscopy was used to examine the morphological changes of the produced TiO2 nanoparticles at various calcination temperatures as well as the precursor ratio. SEM analysis was carried out at 10 kV acceleration Voltage. According to the SEM results, the achievement of high temperatures, the alteration of the precursor ratio, and the presence of distinct contents of the two crystalline phases of titanium dioxide are the causes of the increase in particle size and the apparent aggregation of TiO2 nanoparticles. These results are in agreement with XRD results that showed the particles size of the anatase phase smaller than particles grown at the higher temperature.
References
A. Fujishima, K. Honda, “Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode”, Nature 238 (1972) 37–38.
https://doi.org/10.1038/238037a0.
C. H. Ao, S. C. Lee, “Indoor air purification by photocatalyst TiO2 immobilized on an activated carbon filter installed in an air cleaner”, Chem. Eng. Sci. 60 (2005) 103–109.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2004.01.073.
Y. Paz, “Application of TiO2 photocatalysis for air treatment: patents’ overview”, Appl. Catal. B Environ. 99 (2010) 448–460.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb. 2010.05.011
M. Hussain, N. Russo, G. Saracco, “Photocatalytic abatement of VOCs by novel op timized TiO2 nanoparticles”, Chem. Eng. J. 166 (2011) 138–149.
https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.cej.2010.10.040.
S. Miar Alipour, D. Friedmann, J. Scott, R. Amal, “TiO2/porous adsorbents: recent advances and novel applications”, J. Hazard. Mater. 341 (2018) 404–423.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.07.070.
M. Landmann, E. Rauls, W.G. Schmidt, “The electronic structure and optical response of rutile, anatase and brookite TiO2”, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 24 (2012) 195503.
https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/24/19/195503.
B. L. Diffey, “Sources and measurement of ultraviolet radiation”, Methods 28 (2002) 4-13.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S1046-2023(02)00204-9.
W. J. Yin, S. Chen, J. H. Yang, X. G. Gong, Y. Yan, S. H. Wei, “Effective band gap narrowing of anatase TiO2 by strain along a soft crystal direction”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 96 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3430005 221901.
R. Long, N. J. English, “Band gap engineering of double- cation-impurity-doped anatase-titania for visible-light photocatalysts: a hybrid density functional theory approach”, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13 (2011) 13698–13703.
https://doi.org/10. 1039/C1CP21454C.
S. G. Kumar, L. G. Devi, “Review on modified TiO2 photocatalysis under UV/Visible light: selected results and related mechanisms on interfacial charge carrier transfer dynamics”, J. Phys. Chem. A 115 (2011) 13211–13241, https://doi.org/10.1021/ jp204364a.
J. Godnjavec, J. Zabret, B. Znoj, S. Skale, N. Veronovski, P. Venturini, “Investigation of surface modification of rutile TiO2 nanoparticles with SiO2/Al2O3 on the properties of polyacrylic composite coating”, Prog. Org. Coat. 77 (2014) 47–52.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2013.08.001.
S. Ke, X. Cheng, Q. Wang, Y. Wang, Z. Pan, “Preparation of a photocatalytic TiO2/ZnTiO3 coating on glazed ceramic tiles”, Ceram. Int. 40 (2014) 8891–8895.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.01.027.
R. Phienluphon, K. Pinkaew, G. Yang, J. Li, Q. Wei, Y. Yoneyama, T. Vitidsant, N. Tsubaki, “Designing core (Cu/ZnO/Al2O3)–shell (SAPO-11) zeolite capsule cata lyst with a facile physical way for dimethyl ether direct synthesis from syngas”, Chem. Eng. J. 270 (2015) 605–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.02.071.
Z. Li, Y. Hou, B. Ma, X. Wu, Z. Xing, K. Li, “Super-hydrophilic porous TiO2-ZnO composite thin films without light irradiation”, Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 35 (2016) 1121–1124. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.12308.
Y. Yao, G. Li, S. Ciston, R.M. Lueptow, K.A. Gray, “Photoreactive TiO2/carbon nanotube composites: synthesis and reactivity”, Environ. Sci. Technol. 42 (2008) 4952–4957.
https://doi.org/10.1021/es800191n.
Y. J. Xu, Y. Zhuang, X. Fu, “New insight for enhanced photocatalytic activity of TiO2 by doping carbon nanotubes: a case study on degradation of benzene and methyl orange”, J. Phys. Chem. C 114 (2010) 2669–2676.
https://doi.org/10.1021/ jp909855p.
Y. Liang, H. Wang, H. Sanchez Casalongue, Z. Chen, H. Dai, “TiO2 nanocrystals grown on graphene as advanced photocatalytic hybrid materials”, Nano Res. 3 (2010) 701–705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-010-0033-5.
Y. Zhang, Z.-R. Tang, X. Fu, Y.-J. Xu, “TiO2 graphene nanocomposites for gas-phase photocatalytic degradation of volatile aromatic pollutant: is TiO2 graphene truly different from other TiO2 carbon composite materials”, ACS Nano 4 (2010) 7303–7314.
https://doi.org/10.1021/nn1024219.
J. Liu, H. Bai, Y. Wang, Z. Liu, X. Zhang, D.D. Sun, “Self-assembling TiO2 nanorods on large graphene oxide sheets at a two-phase interface and their anti-recombination in photocatalytic applications”, Adv. Funct. Mater. 20 (2010) 4175-4181. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201001391.
K. Zhou, Y. Zhu, X. Yang, X. Jiang, C. Li, “Preparation of graphene–TiO2 composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity”, New J. Chem. 35 (2011) 353–359.
https://doi.org/10.1039/C0NJ00623H.
J. Auvinen, L. Wirtanen, “The influence of photocatalytic interior paints on indoor air quality”, Atmos. Environ. 42 (2008) 4101-4112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.01.031.
M. Nuño, R. J. Ball, C. R. Bowen, “Study of solid/gas phase photocatalytic reactions by electron ionization mass spectrometry: study of photoreactions by mass spectrometry”, J. Mass Spectrom. 49 (2014) 716-726.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jms. 3396.
M. Nuño, R. J. Ball, C. R. Bowen, R. Kurchania, G. D. Sharma, “Photocatalytic activity of electrophoretically deposited (EPD) TiO2 coatings”, J. Mater. Sci. 50 (2015) 4822-4835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9022-0.
M. Nuño, G. L. Pesce, C. R. Bowen, P. Xenophontos, R. J. Ball, “Environmental performance of nano-structured Ca(OH)2/TiO2 photocatalytic coatings for buildings”, Build. Environ. 92 (2015) 734-742.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2015.05. 028.
P. Wolkoff, G. D. Nielsen, “Organic compounds in indoor air-their relevance for perceived indoor air quality”, Atmos. Environ. 35 (2001) 4407–4417,
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Khyati Mody, I B Patel

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright© by the author(s). Published by journal of Condensed Matter. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.









