Effect of Ge Additive on the Morphological and Physical Properties of Se100-xGex (x = 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 10, 15 and 20) Chalcogenide System
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.61343/jcm.v3i01.95Keywords:
XRD, SEM, Chalcogenide Glasses, Average Coordination Number, Band Gap, Cohesive-energy, optical band gap energy, Mean Bond EnergyAbstract
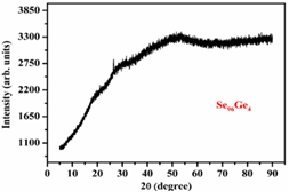
Ge additive chalcogenide materials have become more prevalent in contemporary optoelectronics. The present study utilizes the melt-quenching process for preparing Se-Ge chalcogenide glasses. For the examined system, submicron structural and physical characteristics are examined and described. X-ray diffraction spectra show no characteristic peaks, this indicates that the glassy compositions under investigation are amorphous. A further confirmation of the amorphous nature is provided by SEM. The physical properties of the compositions under examination namely cross-linking density (X), average coordination number (<r>), lone-pair electrons (L), mean bond energy (<E>), constraints (Nc), fraction of floppy modes (f), cohesive-energy (CE), glass transition temperature (Tg), electro-negativity (χ) as well as heat of atomization (Hs) have been deduced in regard to the influence of Ge content. Cohesive-energy is computed using CBA, while mean bond energy is obtained by chemical-bond ordering approach. Shimakawa's relationship was utilized to theoretically compute band gap of the system under investigation. Average single-bond energy, electro-negativity and cohesive-energy were used to analyse the results. A relationship between the mean coordination number and a variety of inferred physical characteristics is established.
References
M. Zemen. J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 4: 426, 1970.
A. H. Clark, Phys. Rev., 154: 750, 1967.
D. N. Payton and W. M. Visscher. Phys. Rev., 154: 802, 1967.
S. C. Moss and J. F. Graczyk. Phys. Rev. Lett., 23: 1167, 1969.
Sharma P and Katyal S C 2008 Phil. Mag. 88 2549.
Kumar K, Thakur N, Bhatt S S and Sharma P 2010 Phil. Mag. 90 3907.
Zhang X H, Guimond Y and Bellac Y 2003 J. Non-Cryst.Solids 519 326.
Shaaban E R 2008 Phil. Mag. 88 781.
Singh G, Sharma J, Thakur A, Goyal N, Saini G S S and Tripathi S K 2005 J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 7 2069.
Anjali, Balbir Singh Patial and Nagesh Thakur Journal of Electronic Materials, 51 (2022) 1089-1096.
Anjali, Balbir Singh Patial, Surya Kant Tripathi and Nagesh Thakur Journal of Electronic Materials, 46 (2017) 1516-1524.
J. Sharma and S. Kumar. Journal of Non-Oxide Glasses, 1: 120-130, 2009.
Anjali, B. S. Patial and N. Thakur. Journal Of Asian Ceramic Societies, 8: 777-792, 2020.
Sharma N, Patial BS, Thakur N. Indian J Pure Appl Phys. 2018;56:128–135.
Thorpe MF. J Non Cryst Solids. 1983;57(3):355–370.
Phillips JC, Thorpe M., Solid State Commun. 985;53(8):699–702.
Saxena M, Kukreti AK, Gupta S, et al., Arch Appl Sci Res. 2012;4:994–1001.
Zhenhua L., J Non-Cryst Solids. 1991;127(3):298–305.
Ticha H, Tichy L, Rysava N, et al. J Non-Cryst Solid. 1985;74(1):37-46.
Tichy L, Ticha H, Mater Lett. 1994;21(3-4):313-319.
Pauling L. J Phys Chem. 1954;58(8):662–666.
Dahshan A, Aly KA. Philos Mag. 2008;88(3):361-372.
Sanderson RT., J Chem Educ. 1952;29(11):539-544.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Anjali, Balbir Singh Patial, Vaishnav Kiran, Nagesh Thakur

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright© by the author(s). Published by journal of Condensed Matter. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.









