A Review Study of Magnetic Nano-Particles Synthesis, Characterization Methods and Applications
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.61343/jcm.v3i02.61Keywords:
Magnetic Nano Particles, Synthesis, Characterization, ApplicationsAbstract
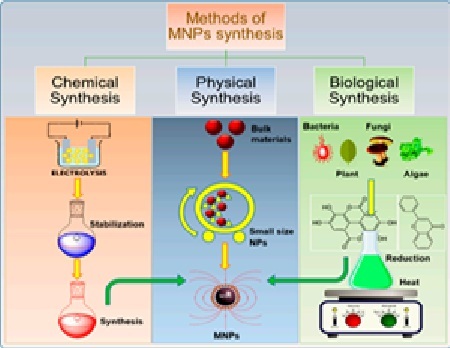
Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) have drawn a lot of interest due to their special qualities, which include large surface area, super para magnetism, and ease of functionalization. These qualities make MNPs perfect for use in electronics, biomedicine, and environmental remediation. This article delivers a critical and nuanced overview, integrating diverse perspectives to advance a deeper understanding of MNP synthesis, characterization, and applications. Typical synthesis methods are covered, such as sol-gel, hydrothermal, thermal decomposition, and co-precipitation. This paper also covers important characterization methods for evaluating the structural and magnetic properties of MNPs, including vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The many uses of MNPs in areas such as environmental pollution control, bio-sensing, and biomedicine are also covered. In addition to offering mechanistic insight into the synthesis, functionalization, and use of MNPs, this thorough analysis also describes the limitations and future possibilities.
References
S Horikoshi and N Serpone, Microwaves in Nanoparticle Synthesis 1stedn (Berlin: Wiley) 2013.
R P Feynman, “There’s plenty of room at the bottom”, Engineering and Science 23, pages 22-36, 1960.
A Ali, T Shah, R Ullah, P Zhou, M Guo, M Ovais, Z Tan and Y Rui, “Review on Recent Progress in Magnetic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Diverse Applications”, Front. Chem.9:629054, 2021.
S K Vashist, “Magnetic Nanoparticles-Based Biomedical and Bioanalytical Applications”, Journal of Nanomedicine & Nanotechnology 04(02) e130, 2013.
J Sun, S Zhou, P Hou, Y Yang, J Weng, X Li and M Li, “Synthesis and characterization of biocompatible Fe3O4 nanoparticles”, Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part AVolume 80A, Issue 2 p. 333-341, 2007.
TK Indira and PK Lakshmi, “Magnetic nanoparticles - A review”, International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Nanotechnology 3, pages 1035–1042, 2010.
Y W Jun, J W Seo and J Cheon, “Nano scaling laws of magnetic nanoparticles and their applicability’s in biomedical sciences”, Accounts of Chemical Research, 41(02), pages 179-189, 2008.
J Kudr, Y Haddad, L Richtera, Z Heger, M Cernak, V Adam and O Zitka, “Magnetic Nanoparticles: From Design and Synthesis to Real World Applications”, Nanomaterials (Basel), 7(9), 243, 2017.
J A L Pérez, M A L Quintela, J Mira, J Rivas and S W Charles, “Advances in the Preparation of Magnetic Nanoparticles by the Microemulsion Method”, The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 101 (41), pages 8045-8047, 1997.
J Mosayebi, M Kiyasatfar and S Laurent, Synthesis, “Functionalization, and Design of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Theranostic Applications”, Advanced Healthcare Materials, 6(23), 2017.
W Wu, Q He and C Jiang C, “Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Surface Functionalization Strategies”, Nanoscale Research Letters. 3, pages 397–415, 2008.
X Wang, J Zhuang, Q Peng and Y Li, “A general strategy for nanocrystal synthesis”, Nature 437(7055), 121-4, 2005.
Y Zheng, C Yao, B Feng and Y Wang, “Synthesis and magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles”. Materials Research Bulletin. 41(3), 2006.
S A M K Ansari, E Ficiarà, F A Ruffinatti, I Stura, M Argenziano, O Abollino, R Cavalli, C Guiot and F D’Agata, “Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Functionalization for Biomedical Applications in the Central Nervous System”, Materials, 12(3), 2019.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Manoj Kumar, Dr. Genius Walia

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright© by the author(s). Published by journal of Condensed Matter. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.









