Molecular Docking Study of Binding of Perylene Di-imide to a Bio Molecular Human Telomeric G-quadruplex
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.61343/jcm.v2i01.49Keywords:
DNA, Duplex, Docking, Telomeric quadruplex, Molecular interactionAbstract
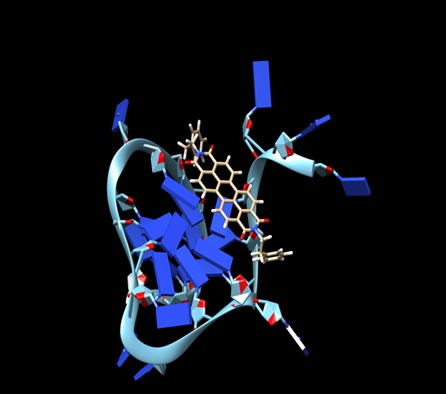
Human telomeres are consisting of d(TTAGGG) repeats involved in the formation of tetraplex DNA structures. Ligands stabilizing these tetraplex DNA structures are potential inhibitors of the cancer cell-associated enzyme telomerase. In human cells, telomerase adds multiple copies of the 5’-GGTTAG-3’ motif to the end of the G-strand of the telomere and in the majority of tumour cells it results over-expressed. Several structural studies have revealed a diversity of topologies for telomeric tetraplexes, which are sensitive to the nature of the cations present, to the flanking sequences, and probably also to concentration, as confirmed by the different conformations deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB). The existence of different polymorphism in the DNA quadruplex and the absence of a uniquely precise binding site give rise to a better understanding of mechanism by verifying with docking methodology approach. To target this, we have selected six different experimental models of the human telomeric sequence d[AG3(T2AG3)3] with the ligands (the perylene di-imide). We simulated out molecular docking of binding of perylene di-imide to a selected G-quadruplex using dock 6.9 to examine the or loop binding mode of perylene di-imide.
The simulation provides the two highest rank docking poses of perylene di-imide i.e. with external strand and groove binding mode; the role different ligand binding is described as external striking on the terminal guanine tetrad and the groove binding. which may be further considered for the study of therapeutic properties of ligand.
References
Alcaro S, Costa G, Distinto S, Moraca F, Ortuso F, Parrotta L, Artese A. The polymorphisms of DNA G-quadruplex investigated by docking experiments with telomestatin enantiomers. Curr Pharm Des. 2012; 18(14):1873-9.
https://doi.org/10.2174/138161212799958495. PMID: 22376115.
Routh ED, Creacy SD, Beerbower PE, Akman SA, Vaughn JP, Smaldino PJ. A G-quadruplex DNA-affinity Approach for Purification of Enzymatically Active G4 Resolvase1. J Vis Exp. 2017 Mar 18;(121):55496.
https://doi.org/10.3791/55496. PMID: 28362374; PMCID: PMC5409278.
Largy E, Mergny JL, Gabelica V. Role of Alkali Metal Ions in G-Quadruplex Nucleic Acid Structure and Stability. Met Ions Life Sci. 2016; 16:203-58. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-21756-7_7.PMID: 26860303.
Sundquist WI, Klug A. Telomeric DNA dimerizes by formation of guanine tetrads between hairpin loops. Nature. 1989 Dec 14; 342(6251):825-9. doi: 10.1038/342825a0. PMID: 2601741.
Sen, D., Gilbert, W. Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis. Nature 334, 364–366(1988). https://doi.org/10.1038/334364a0.
Rawal P, Kummarasetti VB, Ravindran J, Kumar N, Halder K, Sharma R, Mukerji M, Das SK, Chowdhury S. Genome-wide prediction of G4 DNA as regulatory motifs: role in Escherichia coli global regulation. Genome Res. 2006 May; 16(5):644-55. doi:10.1101/gr.4508806. PMID: 16651665; PMCID: PMC1457047.
Faure-Perraud A, Métifot M, Reigadas S, et al. The guanine-quadruplex aptamer 93del inhibits HIV-1 replication ex vivo by interfering with viral entry, reverse transcription and integration. Antiviral Therapy.2011;16(3):383-394. https://doi.org/10.3851/IMP1756.
Feuerhahn S, Iglesias N, Panza A, Porro A, Lingner J. TERRA biogenesis, turnover and implications for function. FEBS Lett. 2010 Sep 10; 584(17):3812-8.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2010.07.032. Epub 2010 Jul 23. PMID: 20655916.
Folini M, Pivetta C, Zagotto G, De Marco C, Palumbo M, Zaffaroni N, Sissi C. Remarkable interference with telomeric function by a G-quadruplex selective bisantrene regioisomer. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Jun 15; 79(12):1781-90.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2010.02.018.Epub 2010 Mar 3. PMID: 20206144.
Sponer J, Cang X, Cheatham TE 3rd. Molecular dynamics simulations of G-DNA and perspectives on the simulation of nucleic acid structures. Methods. 2012 May; 57(1):25-39.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.04.005.Epub 2012 Apr 16. PMID: 22525788; PMCID: PMC3775459.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Mishra V, Tiwari R K

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright© by the author(s). Published by journal of Condensed Matter. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.









