Iron doped MSe2 Monolayers (M=Mo, W): A First-Principles Study of Structural, Electronic, and Magnetic Properties
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.61343/jcm.v2i02.127Keywords:
Doping, Magnetization, Localized effect, SpintronicsAbstract
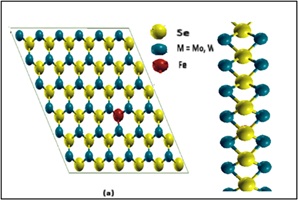
In this study, we examined the effects of iron doping on the electronic and magnetic properties of transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) monolayers, specifically MoSe2 and WSe2, utilizing density functional theory (DFT). Our results demonstrate that strategic doping significantly alters the material properties. Structural analysis reveals that doped systems largely retain the original structure of MSe2ML (Mo, W), despite exhibiting minor lattice distortions. Total energy calculations indicate that these structures remain stable. The doping of Fe induces significant spin polarization in both MoSe2ML and WSe2ML. The spin-down and spin-up channels exhibit distinct band gaps: 1.09 eV (D) and 0.24 eV (I) for MoSe2ML, and 1.0 eV (D) and 0.27 eV (D) for WSe2ML, respectively. Iron doping also induces magnetization in these TMDs. Additionally, the introduction of spin polarization shows that neighbouring atoms around the impurity exhibit slight magnetization due to the localized effects of the dopant. The net magnetic moment for both MoSe2ML and WSe2ML with iron impurities is approximately 2 µB. The computer simulations enable precise doping which leads to improved and tunable properties of TMDs. Future development in electronics, spintronics and quantum computing are facilitated by the potential expansion of doped TMDs.
References
Tiwari, S. de Put, M. L., Sorée, B., Vandenberghe, W.G., “Magnetic order and critical temperature of substitutionally doped transition metal dichalcogenide monolayers”, npj 2D Mater. Appl. 2021, 5, 54.
Fan, X. L.; An, Y. R.; Guo, W. J., “Ferromagnetism in transitional metal doped MoS2 monolayer”, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 154.
Zhao, X.; Chen, P.; Wang, T., “Controlled electronic and magnetic properties of WSe2 monolayers by doping transition-metal atoms”, Superlattices Microstruct. 2016, 100, 252–257.
Cheng, Y.C.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Mi, W.B.; Guo, Z.B.; Schwingenschlögl, U., “Prediction of two-dimensional diluted magnetic semiconductors: Doped monolayer MoS2 systems”, Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2013, 87, 2–5.
Suo, Z. Dai, J. Gao, S and Gao, H, “Effect of transition metals (Sc, Ti, V, Cr and Mn) doping on electronic structure and optical properties of CdS”, Results in Physics, Volume 17, 2020, 103058, ISSN 2211-3797
Min Luo, Shen Yu Hao, and Yin Tai Ling, “Ab initio study of electronic and magnetic properties in ni-doped ws2 monolayer”, AIP Advances, 6(8):085112, 2016.
Mayorga-Martinez, Carmen C., et al. "Transition metal dichalcogenides (MoS2, MoSe2, WS2 and WSe2) exfoliation technique has strong influence upon their capacitance", Electrochemistry Communications 56 (2015): 24-28.
Gao, Jian, et al. "Transition-Metal Substitution Doping in Synthetic Atomically Thin Semiconductors", Advanced Materials, vol. 28, no. 44, Sep. 2016.
K. Dolui, I. Rungger, C. D. Pemmaraju, S. Sanvito, Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 075420.
A. Ramasubramaniam, D. Naveh, Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 195201.
Murtaza, Ghulam, et al. "Chemical vapour deposition of chromium-doped tungsten disulphide thin films on glass and steel substrates from molecular precursors", Journal of Materials Chemistry C 6.35 (2018): 9537-9544.
Chang, Yung-Huang, et al. "Monolayer MoSe2 grown by chemical vapor deposition for fast photodetection" ACS nano 8.8 (2014): 8582-8590.
Zhang, Han, et al. "Strain engineering the magnetic states of vacancy-doped monolayer MoSe2", Journal of Alloys and Compounds 635 (2015): 307-313.
Xie, Ling-Yun, and Jian-Min Zhang. "The structure, electronic, magnetic and optical properties of the Mn doped and Mn-X (X= F, Cl, Br, I and At) co-doped monolayer WS2: a first-principles study", Journal of Alloys and Compounds 702 (2017): 138-145.
Zhao, Xu, et al. "Electronic and magnetic properties of Mn-doped monolayer WS2", Solid State Communications 215 (2015): 1-4.
Nayak, P. K., Horbatenko, Y., Ahn, S., Kim, G., Lee, J. U., Ma, K. Y., ... & Shin, H. S. (2017). “Probing evolution of twist-angle-dependent interlayer excitons in MoSe2/WSe2 van der Waals heterostructures”, ACS nano, 11(4), 4041-4050.
Gong, Y., Lei, S., Ye, G., Li, B., He, Y., Keyshar, K., ... & Ajayan, P. M. (2015), “Two step growth of two-dimensional WSe2/MoSe2 heterostructures”, Nano letters, 15(9), 6135- 6141.
Charapale, Mahesh R., et al. "Enhancing capacitive performance of MoS2 through Fe doping: Synthesis, characterization, and electrochemical evaluation for supercapacitor applications", Surfaces and Interfaces 52 (2024): 104814.
Liu, C., Wu, K., Meng, G., Wu, J., Peng, B., Hou, J., ... & Guo, X. (2017). “Explore the properties and photocatalytic performance of iron-doped g-C3N4 nanosheets decorated with Ni2P”, Molecular Catalysis, 437, 80-88.
Jafari, M., Rahmani-Ivriq, N., & Dyrdal, A. (2024), “Effect of Fe-doping on VS2 monolayer: A first-principles study”, arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.12001.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Lalita Devi, Arun Kumar, Anjna Devi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright© by the author(s). Published by journal of Condensed Matter. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.









