“Paper and Inks”: Sustainable Sensing Through Development of Paper Platforms
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.61343/jcm.v3i01.110Keywords:
Paper platform, Carbon Nanotubes, ePADs, Electrochemical sensors, Cyclic VoltammetryAbstract
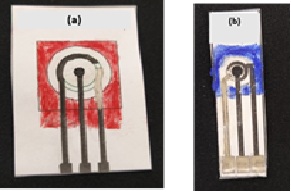
The platform of biosensor plays a pivotal role in the efficacy of detection; therefore, the selection of an optimal material that meets all requisite criteria is essential. Paper as a platform for sensing application exhibit additive attributes over the other commercially available substrates as it might fulfils the ‘REASSURED’ benchmark introduced under WHO guidelines. The study entails the fabrication of an electrochemical biosensing platform using regular office paper with different GSM thickness (75, 85,120 and 140 GSM). The conductive inks, paper thickness, design pattern, hydrophobic layer and connection materials were iterated and optimized through multiple scans of cyclic voltammetry. A simplified design of three electrode system having reference and working electrode at an optimized distance of around 1mm, resulted in reduced ohmic resistance. The concentration and number of layers of conductive inks were optimized through conductivity measurements which lie between 1Ω to 4 Ω for reference electrode and 0.0005 MΩ to 0.025 MΩ for counter electrode. Working electrode was fabricated using two differently modified conductive CNTs ink where conductivity varied for PCNT as 0.06 kΩ to 0.1 kΩ while LCNT varied 0.014 kΩ to 1.33 KΩ. Beside this an ecofriendly volatile organic compound free hydrophobic reagents were also tested for fabricating the sensing region. The CV scans show stability of adsorbed conducting materials on the fabricated paper platform stating that the platform could be further evaluated for biosensing application.
References
K. J. Land, D. I. Boeras, X. S. Chen, A. R. Ramsay, and R. W. Peeling, “REASSURED diagnostics to inform disease control strategies, strengthen health systems and improve patient outcomes,” Nature Microbiology, vol. 4, no. 1, 2019, doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0295-3.
S. R. Benjamin, F. de Lima, V. A. do Nascimento, G. M. de Andrade, and R. B. Oriá, “Advancement in Paper-Based Electrochemical Biosensing and Emerging Diagnostic Methods,” Biosensors, vol. 13, no. 7, 2023, doi: 10.3390/bios13070689.
A. E. Ferreira de Oliveira, A. César Pereira, and L. F. Ferreira, “Fully handwritten electrodes on paper substrate using rollerball pen with silver nanoparticle ink, marker pen with carbon nanotube ink and graphite pencil,” Analytical Methods, vol. 14, no. 19, 2022, doi: 10.1039/d2ay00373b.
G. Ebrahimi, P. S. Pakchin, A. Mota, H. Omidian, and Y. Omidi, “Electrochemical microfluidic paper-based analytical devices for cancer biomarker detection: From 2D to 3D sensing systems,” Talanta, vol. 257, 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2023.124370.
A. M. Díez-Pascual, “Carbon-based nanomaterials,” International Journal of Molecular Sciences, vol. 22, no. 14, 2021, doi: 10.3390/ijms22147726.
J. R. Camargo et al., “Development of conductive inks for electrochemical sensors and biosensors,” Microchemical Journal, vol. 164, p. 105998, May 2021, doi: 10.1016/J.MICROC.2021.105998.
P. G. Karagiannidis et al., “Microfluidization of Graphite and Formulation of Graphene-Based Conductive Inks,” ACS Nano, vol. 11, no. 3, 2017, doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b07735.
Y. Tian et al., “Improved resistance stability of transparent conducting films prepared by PEDOT: PSS hybrid CNTs treated by a two-step method,” Materials Research Express, vol. 6, no. 11, 2019, doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab46ea.
Y. Tian et al., “High-performance transparent pedot: Pss/cnt films for oleds,” Nanomaterials, vol. 11, no. 8, 2021, doi: 10.3390/nano11082067.
S. V. Mamykin, I. B. Mamontova, T. S. Lunko, O. S. Kondratenko, and V. R. Romanyuk, “Fabrication and conductivity of thin PEDOT: PSS-CNT composite films,” Semiconductor Physics, Quantum Electronics and Optoelectronics, vol. 24, no. 2, 2021, doi: 10.15407/spqeo24.02.148.
T. Xue et al., “Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube-N-Doped Graphene/Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):Poly(styrenesulfonate) Nanohybrid for Electrochemical Application in Intelligent Sensors and Supercapacitors,” ACS Omega, vol. 5, no. 44, 2020, doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c02224.
H. U. Rehman et al., “Stretchable, strong and self-healing hydrogel by oxidized CNT-polymer composite,” Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, vol. 90, pp. 250–260, Nov. 2016, doi: 10.1016/J.COMPOSITESA.2016.07.014.
X. He, J. Shi, Y. Hao, L. Wang, X. Qin, and J. Yu, “PEDOT:PSS/CNT composites based ultra-stretchable thermoelectrics and their application as strain sensors,” Composites Communications, vol. 27, p. 100822, Oct. 2021, doi: 10.1016/J.COCO.2021.100822.
N. Agrawal, D. Bhagel, P. Mishra, D. Prasad, and E. Kohli, “Post-synthetic modification of graphene quantum dots bestows enhanced biosensing and antibiofilm ability: efficiency facet,” RSC Advances, vol. 12, no. 20, 2022, doi: 10.1039/d2ra00494a.
C. Hassam and D. A. Lewis, “Dispersion of single and multiwalled nanotubes with poly(sodium styrene sulfonate) - Effect of pH and ionic strength on dispersion stability,” Australian Journal of Chemistry, vol. 67, no. 1, 2014, doi: 10.1071/CH13350.
S. E. Moya, A. Ilie, J. S. Bendall, J. L. Hernandez-Lopez, J. Ruiz-García, and W. T. S. Huck, “Assembly of polyelectrolytes on CNTs by Van der Waals interactions and fabrication of LBL polyelectrolyte/CNT composites,” Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics, vol. 208, no. 6, 2007, doi: 10.1002/macp.200600530.
N. Agrawal, S. Gaur, K. V. Mani, and R. Arora, “Carbon Nanotubes/Polyurethane Foam for Noise Passivation at 4000 Hz,” ACS Applied Nano Materials, vol. 7, no. 1, 2024, doi: 10.1021/acsanm.3c03866.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ayushi Singh, Neha Agrawal, Niroj Kumar Setthy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright© by the author(s). Published by journal of Condensed Matter. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.









